AR in Industry
The same augmented reality (AR) technology that is making advances in consumer markets also has great potential to be used in industry. AR enables a new information-delivery paradigm where digital information is superimposed directly on a physical object or environment.
Leading manufacturers are implementing AR to visualize, instruct and interact with machines and people. This is helping to address inefficiencies throughout the entire value chain from engineering to production and service.
Visualize
Visualizing is a practice that helps you focus your thoughts on something positive. It can be a powerful way to relieve stress and increase your confidence. It can also help you get in the right frame of mind to complete a task or achieve a goal.
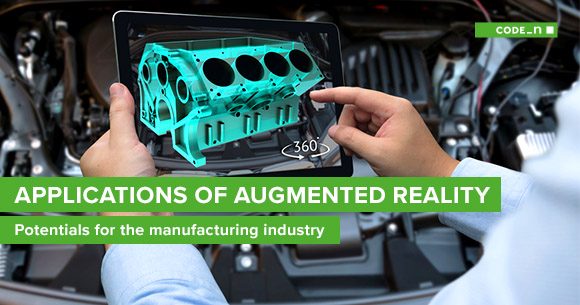
In the context of ar in industry, visualization can mean a variety of things, from simply seeing what a new product will look like to interacting with 3D models. For example, a car manufacturer could use AR to display an engine disassembled in an interactive, animated model. This model can be rotated and zoomed in for a better view, and it can be used to guide the technician through each step of the procedure.
Another application of AR is for quality assurance. Workers can compare the original with the virtual model to see whether there are deviations that need to be corrected before production begins. This can improve efficiency and speed up quality inspection by eliminating the need to transfer data into manuals.
Manufacturing processes with high variation and long standard cycle times are ideal candidates for using augmented reality. By standardizing and digitizing work instructions, companies can eliminate error-prone manuals and provide workers with an exact template of what to produce.
For example, when a worker is building a headliner in automotive manufacturing, they need to know where to place padding, glue and wire harnesses to match the model. With digitized work instructions, these placements can be mapped out onto the headliner so workers can follow them without having to make a mistake.
Similarly, in the case of aerospace and defense manufacturing, companies can standardize their work instructions and provide workers with an exact template of what they need to produce. By standardizing and digitizing work instructions, organizations can eliminate errors and reduce process time.
Another use of AR in industry is for safety, introducing new employees to the workplace safely and interactively. By using 3D models, holograms of equipment and virtual representations of workflows, AR can help new employees understand the equipment and environment, the role and responsibilities of team members and potential safety hazards. The system can also provide instant feedback on employee performance, incentivizing workers to complete tasks quickly and accurately.
Instruct/Guide
AR manuals are digital guides that offer hands-free access to augmented expert guidance. Whether they are user manuals, maintenance apps, unboxing apps or problem-solving applications, these guides use 3D object recognition and image matching technologies to create interactive augmented reality instructions that make complex equipment and processes easier for people to understand.
These instructions can be viewed on most modern mobile and tablet devices, HMDs such as Microsoft’s HoloLens or AR glasses like Meta. Typically, they include visual elements such as blinking lights, audio cues and animations to draw attention to the instructions.
Using guided AR for training and retraining is easy and fast. Workers ar in industry in a training session can view the steps on an AR system as they work on a production line, picking up the process faster and without error.
It also ensures that the information is consistent across an enterprise, no matter where it was last updated. With connected systems, work instructions can be updated in one click, preventing lapses in information.
In aerospace and defense manufacturing, digitized work instructions help reduce errors and ensure quality. In the case of headliners, for example, workers need to know where to lay padding, glue and wire harness. The placements need to be exact to match the model they are working on.
When an inspection process is done incorrectly, it can lead to a faulty product and increased downtime. Fortunately, augmented reality inspection solutions can incorporate quick inspections at any step of the process without affecting cycle time.
Augmented reality software can also be used to ensure that workers don’t move forward until they have completed each step of the process, ensuring accuracy. This prevents workers from missing steps and causing mistakes on the final assembly.
These augmented reality instructions can be created with a drag-and-drop interface, eliminating the need for technical expertise. They can be customized to include additional sensory features, including audio cues and blinking lights, that increase worker awareness.
AR guides and inspections speed service calls, improve first-time fix rates and reduce customer downtime. They also allow manufacturers to gather data from the field and integrate it with process data for a more complete picture of operation and production. They are especially effective when combined with automated process augmentation, bringing both processes together to work seamlessly.
Interact
AR technology in industry creates business value by making it possible to interact with computer-generated information within the real world. Unlike virtual reality, which disengages users from the real world and substitutes a virtual environment for it, AR displays integrate an immersive computer-generated experience into the physical world, bringing together the two in ways that make them naturally flow as one.
In the manufacturing sector, AR can be used to enhance workplace safety and improve processes. Companies like Cisco and Siemens develop industrial AR solutions that provide workers with real-time information, performance metrics, and guidance on assembling components. These solutions reduce downtime and improve worker productivity, reducing costs and creating safer and healthier work environments.
Moreover, companies that design products and services can use AR to help customers understand and purchase their products. For example, Sephora uses an app to let customers try on makeup before purchasing it, and Wayfair uses an iPad app that lets shoppers browse furniture in 3D.
The technology also allows companies to provide more detailed and feature-rich instructions and documentation to potential customers. For example, a coffee machine can offer an interactive virtual manual that provides instructions on how to brew coffee. This type of experience is an important step in the customer journey and can be especially useful in the travel and tourism industries, where consumers are often looking to get a sense of the products and service they are buying before making a final decision.
Businesses can also use AR to communicate with employees in more detailed and interactive ways. A new approach to ar in industry employee training involves delivering instructions through AR, which can provide visual or auditory cues when an employee completes each step in a process correctly. This feedback can be especially helpful in training new or less-experienced workers.
To scale AR across an entire organization, firms must have the ability to publish digital content on demand through a general-purpose software application that runs on AR devices. This method provides reliable, high-resolution experiences and is especially valuable when frequent changes to the content are necessary.
Share
In the manufacturing world, augmented reality (AR) comes in various guises. For instance, augmented reality can be implemented in the form of virtual avatars, or holograms that mimic real-world objects and people. This allows users to interact with AR apps and other digital content without the need for physical input such as a keyboard or mouse.
In industry, the most valuable use of AR is in enhancing human performance on the jobsite. A well-designed AR app can help workers with a myriad of tasks from selecting and placing a component to completing a task with minimal supervision. For instance, a factory floor worker using an AR app can view an animated diagram of a complex machine in a matter of seconds. Other high-impact uses include augmenting traditional instruction such as training videos and guiding employees through large industrial buildings.
One of the most impressive applications of AR is in identifying and tracking assets in real-time. For example, a maintenance technician could point to a computer server and see its status as well as what it needed to do its job. As a result, the company can prioritize its resources in a way that improves customer service and reduces costs and risk.